CMDB in 30 days: method and templates
Estimated reading time: 9 minutes
Key Takeaways
-
- Understanding a CMDB (Configuration Management Database) is crucial for modern ITSM, offering a single source of truth for assets, processes, and dependencies (source).
-
- Automation dramatically improves accuracy and efficiency, enabling real-time asset discovery and relationship mapping across the IT estate (CMDB automation guide).
-
- ITIL 4 alignment ensures your CMDB supports robust change, incident, and problem management processes (ServiceNow – What is CMDB?).
-
- Iterative, best-practice-based implementation with defined ownership, integration, and regular audit cycles produces sustainable value and compliance.
- Step-by-step templates and real examples—plus support from tools like Halo ITSM—can accelerate time-to-value so your team achieves CMDB success in just 30 days.
What is a CMDB? Understanding the Configuration Management Database
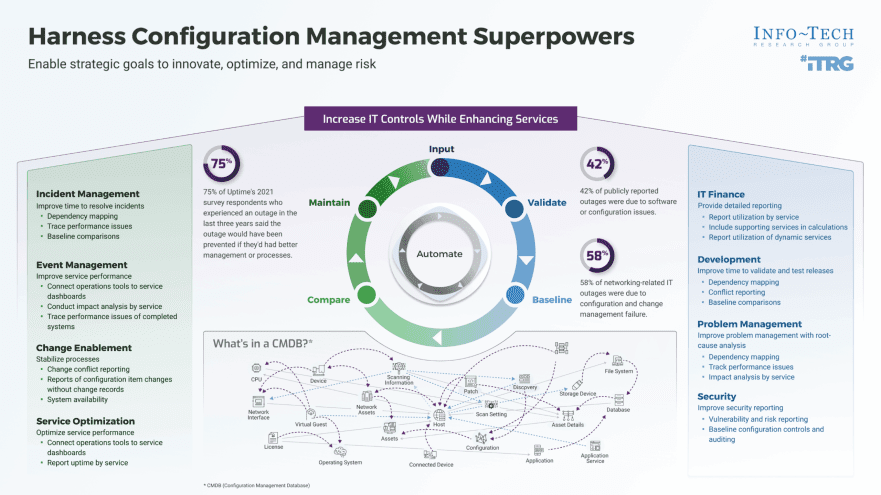
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a cornerstone of effective IT Service Management. At its core, a CMDB is a central repository that meticulously catalogs all your organization’s configuration items (CIs)—hardware, applications, documents, personnel, and more (source, source).
It records not just the type and location of each configuration item, but also its relationships, ownership, and history. This interconnected mapping becomes the backbone for strategic processes—enabling smarter change management, incident management, problem management, and compliance efforts (source).
-
- Catalog every server, network device, and software asset—down to OS and version info.
-
- Map relationships, including application dependencies that span your entire digital environment.
- Track licenses and users for governance and compliance.
“A CMDB isn’t just a record—it’s the organizational map that IT teams rely on every single day to diagnose, analyze, and improve.”
What is stored in a CMDB?
Everything about your IT assets (CIs): state, location, owners, and all relationships.
Learn more: Ivanti—What is a CMDB?
How Does a CMDB Work? Data Collection, Automation & Relationship Mapping
A modern CMDB merges cmdb automation and manual review to keep your configuration data up to date (source).
-
- Automation scans your environment, finds new or changed CIs, and maps them—reducing the risk of errors and outdated info.
- Manual entry fills in complex or nuanced fields requiring human judgment.
Your CMDB then displays dynamic relationship maps—so, for example, a mobile app’s backend dependencies are all visually linked for impact and root cause analysis.
“Staying accurate is a never-ending process—automated reconciliation, scheduled audits, and real-time alerts ensure your CMDB reflects current reality.”
Platforms like ServiceNow, ManageEngine, Atlassian, and Halo ITSM use these principles for ongoing accuracy. If you want a hands-off approach, see how Halo ITSM asset discovery tools automate CMDB collection for you.
How does a CMDB keep information up to date?
Automated discovery and scheduled audits ensure all asset and relationship info is current, every day.
See more in ServiceNow’s CMDB doc
CMDB and ITIL 4: Aligning Your Configuration Management
To make your CMDB truly effective, align it with cmdb itil4 principles. The ITIL 4 standard and the Common Service Data Model (CSDM) let you:
-
- Map IT services precisely to your infrastructure and business functions.
-
- Predict service impact before changes go live, improving reliability.
-
- Streamline audit trails for compliance—reducing surprises at audit time.
- Enable rapid root cause analysis that minimizes service outages (source).
For an applied look, see how Halo ITSM vs ServiceNow platforms handle ITIL workflows and CSDM in real-world scenarios.
How does a CMDB fit into ITIL 4 processes?
The CMDB is the backbone of configuration management under ITIL4, connecting all the dots for seamless change, incident, and problem management. If you want CMDB scope + governance translated into actual workflows and tool rules, see how our ITIL v4-certified engineers deliver ITSM implementation across CMDB, change, and incident practices.
In-depth ITIL4 and CMDB with ServiceNow
CMDB Best Practices for Configuration Items and Automation
Following proven cmdb best practices is the fastest way to sustainable, low-maintenance results (source).
-
- Define Clear Objectives: Start with your org’s top priorities and align your CMDB with them.
-
- Start Small: Focus first on critical, high-impact CIs and expand from success.
-
- Use Automation: Set up discovery tools to minimize manual mistakes—and read about Halo ITSM automated data reports for KPI dashboards and expert tips.
-
- Audit Regularly: Clean up data, de-duplicate, and verify records to prevent drift.
-
- Assign Ownership: Make sure every CI or CI group has a clear owner or team for accountability.
- Integrate End-to-End: Connect your CMDB with all ITSM processes for full lifecycle visibility (source).
Common Pitfalls:
-
- t
- Trying to document every asset on day one causes frustration and project stall.
-
- Skipping scheduled data validation leads to inaccurate, brittle data.
- Lack of buy-in from other teams slows down adoption and success.
Best practices in summary:
-
- Clear objectives and manageable initial scope
-
- Automate discovery wherever possible
-
- Ongoing audits and shared ownership
- Integrated ITSM workflows
Explore more best practices: Ivanti CMDB glossary
CMDB Automation: Increasing Accuracy and Efficiency
CMDB automation is your #1 tool for eliminating manual drudgery and keeping data fresh (source).
-
- Higher Accuracy: Remove manual typos forever with system-driven updates.
-
- Realtime Speed: Onboard and update assets as soon as they appear.
- Complete Coverage: Scalable to even the largest cloud and hybrid IT estates (source).
Popular tools:
-
- Enterprise: ServiceNow Discovery, BMC Discovery, ManageEngine, HaloITSM
- Open-source: Ansible, Puppet, custom connectors (source)
Typical workflow:
-
- Scheduled or event-triggered scans
-
- Automatic relationship mapping
- APIs connecting the CMDB to all your ITSM tools
What is CMDB automation and why is it important?
The use of tools to auto-discover, onboard, and maintain all your config data for peak efficiency and accuracy. The result? No more stale records—and scalable, reliable processes at any enterprise size.
Detailed explanation: ServiceNow’s CMDB tools
CMDB Examples: Real-World Use Cases, Platforms, and Success Stories
How do real organizations leverage their CMDBs? Here are some prime cmdb examples (source, source):
-
- Change Impact Analysis: Use the CMDB before every major rollout to predict downstream impacts and proactively resolve risks.
-
- Incident Management: Map every affected system instantly when an outage strikes, so teams cut incident TTR dramatically.
- Auditing & Compliance: Pull complete, timestamped records for every configuration change for any auditor at any time.
Success stories:
-
- Organizations migrating to the cloud use CMDBs to map dependencies, ensuring zero downtime.
- IT integrations after mergers/acquisitions become far smoother and safer thanks to full asset transparency.
Want a practical setup? Dive into the Halo ITSM asset discovery tools guide for hands-on CMDB configuration and mapping tips.
What are real-world examples of using a CMDB?
Ecommerce, financial, and enterprise IT teams all rely on CMDBs for secure deployments, rapid root cause analysis, and successful digital overhauls.
See more use cases: ServiceNow CMDB
CMDB Tutorial: Step-by-Step Configuration Management Database Implementation
This actionable cmdb tutorial distills years of experience into a proven, fast-track roadmap (source):
-
- Step 1 – Identify CIs: Make a comprehensive, prioritized list of your hardware, software, and business-essential assets.
-
- Step 2 – Select a CMDB Tool: Choose one that meets your needs—scalability, ITSM integration, automation. See comparisons like Halo ITSM vs Freshservice pricing/features.
-
- Step 3 – Automate Asset Discovery: Deploy scan tools and schedule regular auto-updates (source).
-
- Step 4 – Map Relationships: Document all infrastructure and application dependencies, using visual diagrams where possible (Atlassian CMDB Guide).
-
- Step 5 – Assign Data Ownership: Ensure every CI group has a clearly responsible team or role (source).
-
- Step 6 – Integrate with ITSM Suites: Hook up incident, change, problem, and asset management modules for maximum value (source). See also SMC products overview.
-
- Step 7 – Build Governance and Access Controls: Set user permissions, CI edit rights, and logging/auditing to enforce integrity (source).
- Step 8 – Maintain and Optimize: Schedule periodic reviews, reconciliation, and continuous improvement cycles (source).
For Halo ITSM specifics, review the detailed CMDB setup guide crafted for rapid time-to-value.
Summary checklist:
-
- List CIs – prioritize by business need
-
- Choose/install a CMDB platform
-
- Automate import/discovery
-
- Map all relationships
-
- Assign ownerships
-
- Connect ITSM workflows
-
- Lock down access/governance
- Audit and improve, always
View implementation details: Atlassian’s CMDB Guide
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a CMDB and why is it important?
A CMDB, or Configuration Management Database, is a central system that records every IT asset (configuration item), relationships, and state—ensuring reliability and integrity for all your ITSM processes.
All your IT assets (hardware, software, docs, users), their state, ownership, locations, and every relationship between them.
How does a CMDB keep information up to date?
Through automated discovery tools plus regular, scheduled data audits, so nothing falls out of sync.
How does a CMDB fit into ITIL 4 processes?
The CMDB underpins all config management, serving as the link between assets and ITIL processes like change, incident, and problem management.
What are best practices for setting up a CMDB?
-
- Define goals and business value
-
- Start small and iterate
-
- Automate collection/updates
-
- Assign owners, audit often
- Integrate with ITSM
What is CMDB automation and why is it important?
Automation uses software to discover assets and keep records updated—removing manual effort, improving accuracy, and enabling scale.
What are real-world examples of using a CMDB?
-
- Ecommerce sites mapping dependencies for safe rollouts
-
- Banks resolving outages rapidly thanks to CI mapping
- Enterprises using CMDBs for risk-free cloud migrations
How do I set up a CMDB from scratch?
-
- List critical assets
-
- Select/install a tool
-
- Automate import
-
- Map relationships
-
- Assign owners
-
- Link to ITSM
-
- Define control policies
- Audit and enhance
What are the next steps after learning about CMDB?
Define your organization’s configuration objectives, select the right tool, deploy automation, get buy-in, and commit to ongoing improvement for ITSM success.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways for Effective CMDB Implementation and Next Steps
Getting your CMDB right—within 30 days, with the right method and templates—is entirely possible. With clear goals, automation, cross-team buy-in, and a focus on regular improvement, your organization secures lasting value, transparency, and powerful ITSM practices (source).
Review vendor documentation, invest in ITIL 4-aligned tools and practices, or connect with trusted ITSM consultants to tailor the roadmap for your unique needs. Your CMDB will thank you—and reward your business—with reliability and confidence for years to come.
For deeper dives and the latest thinking, see OpenText’s CMDB overview or the comprehensive ServiceNow CMDB resource library.