Dans le domaine de la gestion de projet Scrum, le sprint agile est devenu une méthode de premier plan pour optimiser le travail d’équipe, améliorer le développement de fonctionnalités et atteindre rapidement les objectifs. Un sprint se déroule sur une période fixe, généralement de deux à quatre semaines, et se concentre sur un ensemble d’éléments (tickets, user stories) issus du backlog produit. Cette approche permet à l’équipe de se concentrer sur des tâches claires, de mesurer régulièrement les progrès et d’ajuster le plan au fur et à mesure du déroulement du processus. Découvrez comment mettre en œuvre un sprint agile, ses étapes clés, les rôles de chaque membre de l’équipe et les meilleures pratiques à adopter pour renforcer votre gestion de projet.
Comprendre le sprint agile dans la gestion de projet Scrum
Le sprint est l’unité de base de la méthodologie agile Scrum. Il s’agit d’une période de temps définie pendant laquelle l’équipe se concentre sur le développement de fonctionnalités spécifiques afin de produire une version potentiellement livrable du produit. Contrairement aux approches traditionnelles en cascade, le sprint agile favorise une gestion itérative et incrémentale. Cette approche offre une meilleure visibilité, une adaptation rapide et une plus grande cohésion d’équipe.
- Objectif : Créer un incrément de produit fonctionnel et testable.
- Durée : Période fixe (souvent deux semaines), appelée timebox.
- Livrable : Un ensemble de fonctionnalités entièrement développées, prêtes pour la présentation.
En se concentrant sur des sprints courts, l’équipe a un meilleur contrôle sur la gestion de projet, s’appuie sur des outils (comme Trello ou monday.com) pour organiser ses tickets et peut affiner le backlog produit au fur et à mesure.

Vous souhaitez accélérer votre transformation numérique ?
Définition et rôle du sprint en Scrum
Un sprint en Scrum est un cycle de travail qui vise à transformer une partie du backlog produit en un incrément fonctionnel. Le sprint est au cœur de la méthodologie agile, car il établit un rythme régulier pour la planification, l’exécution du développement, la revue et l’amélioration continue.
Chaque sprint commence par la Planification du Sprint, durant laquelle l’équipe sélectionne les éléments prioritaires du backlog. Ces éléments (tickets, stories) correspondent à des fonctionnalités à haute valeur ajoutée pour le client ou l’utilisateur final. À la fin de chaque sprint, un produit partiel (mais potentiellement livrable) est présenté lors de la Revue de Sprint, puis l’équipe tire les enseignements nécessaires du sprint.
Les étapes clés d'un sprint agile
1. Planification (sprint planning)
La réunion de planification du sprint réunit le Scrum Master, le Product Owner et l’équipe de développement. Son objectif est de définir le périmètre du sprint et d’établir le plan de travail. Le Product Owner présente le backlog, met en évidence les éléments prioritaires et clarifie leurs définitions . L’équipe discute ensuite de la faisabilité, estime la charge de travail (story points) et identifie les tâches nécessaires.
- Entrées : Backlog produit, objectifs à court terme, ressources disponibles.
- Sorties : Un backlog de sprint clair, un objectif de sprint défini, un plan de développement.
- Outils utiles : monday.com, tableaux Kanban pour visualiser les tâches.
2. Exécution des tâches du sprint
Pendant la phase d’exécution, l’équipe de développement se concentre sur la réalisation des tâches identifiées. Les membres de l’équipe travaillent en étroite collaboration, communiquent régulièrement et ajustent leur charge de travail en conséquence. Les réunions quotidiennes Scrum leur permettent de suivre l’avancement, d’identifier les obstacles et de réorienter le travail si nécessaire.
- Bonnes pratiques : Communication ouverte, réactivité, solidarité entre les membres de l’équipe.
- Outils : Tableaux de tâches, backlog de sprint, tableaux de suivi en ligne (monday.com, Trello).
3. La revue de sprint
- Focus : Démonstration des fonctionnalités développées.
- Feedback : Recueil de commentaires constructifs, identification des axes d’amélioration.
4. La rétrospective (rétrospective de sprint)
La dernière étape du sprint, la rétrospective, permet à l’équipe de réfléchir à ses propres performances. Qu’est-ce qui s’est bien passé ? Quels obstacles ont entravé les progrès ? Quels ajustements doivent être apportés pour les futurs sprints ? Cette réunion est essentielle pour établir une culture d’amélioration continue, renforcer la cohésion de l’équipe et affiner le processus.
- Objectif : Optimiser le processus, améliorer la communication.
- Résultats attendus : Un plan d’action concret pour accroître l’efficacité des futurs sprints.
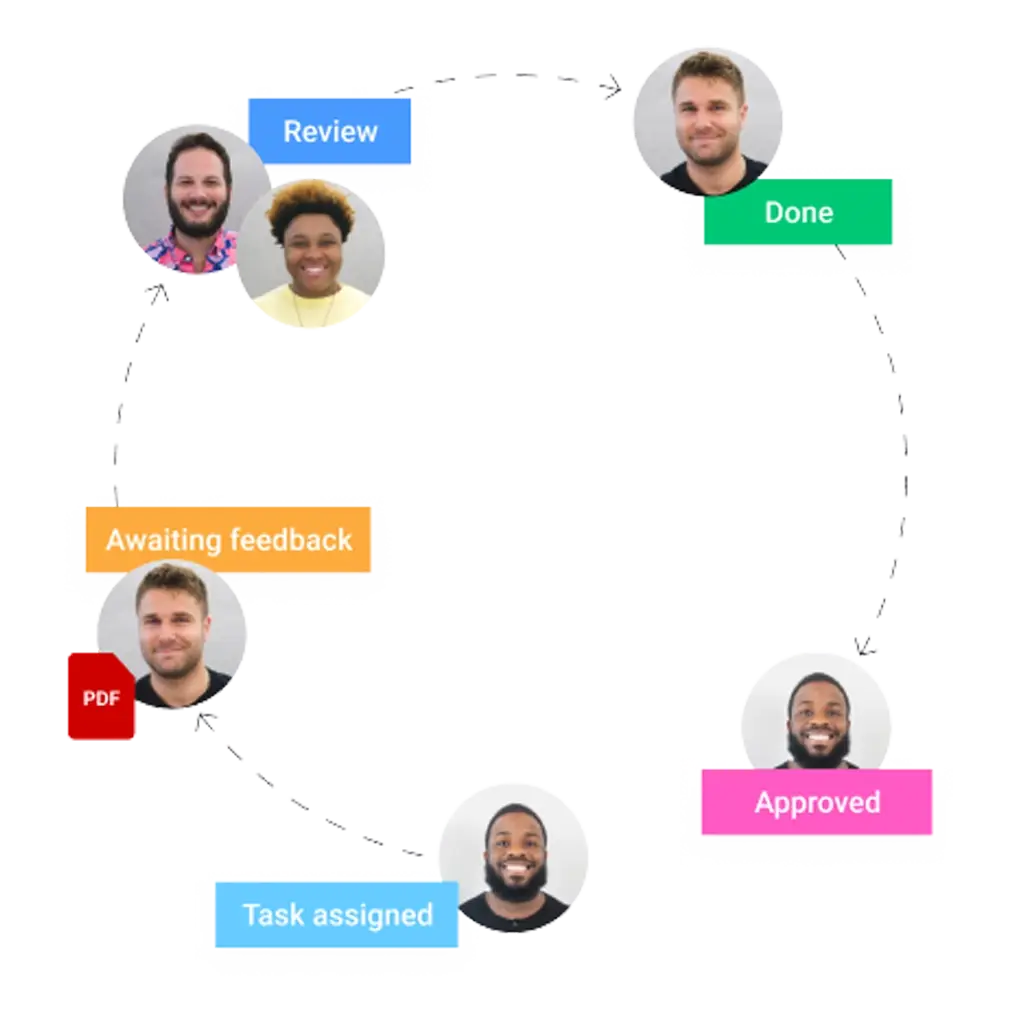
Obtenez une démonstration personnalisée de monday.com
Rôles dans un sprint agile : Scrum Master, Product Owner et équipe de développement
Le succès d’un sprint dépend de rôles clairement définis, chaque personne ayant ses responsabilités dans la gestion du projet.
Le Scrum Master
Le Product Owner
L'équipe de développement
L’équipe de développement est chargée de transformer les éléments du backlog en fonctionnalités opérationnelles. Ses membres s’organisent de manière autonome, estiment la charge de travail et s’engagent à atteindre des objectifs clairs pendant le sprint.
Meilleures pratiques pour un sprint agile efficace
Pour maximiser l’efficacité d’un sprint agile, quelques bonnes pratiques doivent être suivies :
- Clarté des objectifs : Définir un objectif de sprint précis et compréhensible pour l’ensemble de l’équipe.
- Priorisation rigoureuse : Choisir les éléments du backlog ayant la plus forte valeur ajoutée.
- Transparence : Utiliser des outils de suivi (monday.com, tableaux Kanban) pour rendre visible l’avancement des tâches.
- Communication ouverte : Encourager les échanges, le feedback et la résolution rapide des problèmes.
- Adaptabilité : Ajuster le plan en fonction des événements imprévus, sans perdre de vue l’objectif.
- Rétrospective régulière : Tirer les leçons de chaque sprint pour améliorer continuellement le processus.
Indicateurs de succès : comment mesurer l'efficacité d'un sprint agile ?
Pour évaluer le succès d’un sprint, il est essentiel de suivre les indicateurs clés de performance (KPI) afin de mesurer la performance et la qualité du travail effectué :
- Vélocité : Nombre de points d’histoire terminés dans le sprint.
- Taux d’atteinte des objectifs : Pourcentage de fonctionnalités terminées par rapport au plan.
- Qualité du livrable : Nombre de bugs identifiés, niveau de satisfaction du Product Owner et des utilisateurs.
- Amélioration continue : Mise en œuvre des actions identifiées lors de la rétrospective.
L’analyse de ces indicateurs contribue à améliorer la gestion de projet et garantit que l’équipe exploite au mieux le potentiel du sprint agile.
FAQ sur les sprints dans la méthodologie agile
Un sprint est un cycle de travail itératif et limité dans le temps (souvent deux semaines) en Scrum. Pendant ce temps, l’équipe se concentre sur un ensemble de fonctionnalités du backlog produit afin de livrer un incrément fonctionnel et testable.
Un sprint commence par une réunion de planification (Sprint Planning) pour définir l’objectif et la portée du sprint. L’équipe exécute ensuite les tâches, avec des points de contrôle quotidiens (Daily Scrum) pour ajuster le travail. À la fin du sprint, une revue de sprint présente les fonctionnalités développées, suivie d’une rétrospective pour améliorer le processus.
Les erreurs courantes incluent un backlog mal hiérarchisé, un objectif de sprint vague, une mauvaise communication au sein de l’équipe et une rétrospective bâclée. Il est également important d’éviter de modifier la portée du sprint en cours de sprint afin de maintenir la stabilité du plan.
Le succès se mesure à l’atteinte des objectifs fixés, à la qualité du livrable, à la satisfaction des parties prenantes et à la capacité de l’équipe à s’améliorer d’un sprint à l’autre. Des indicateurs tels que la vélocité, le respect des objectifs du sprint et la réduction des bugs permettent de suivre les progrès.
Des outils tels que monday.com, Trello et Asana facilitent la gestion des sprints en offrant une vue claire du backlog, des tâches en cours et des indicateurs de progression. Ces plateformes vous permettent de visualiser le flux de travail, de suivre les progrès en temps réel et d’améliorer la communication au sein de l’équipe.
En adoptant un sprint agile, vous pouvez transformer votre gestion de projet. Vous gagnerez en flexibilité, en visibilité sur l’avancement des travaux et améliorerez la qualité de vos livrables. Les sprints agiles, soutenus par une bonne planification, un backlog clair et des outils efficaces, sont un guide fiable pour la réussite des projets.
Boostez votre efficacité opérationnelle avec nos solutions numériques sur mesure !
Chez SMC Consulting, nous comprenons que chaque entreprise est unique. C’est pourquoi nous proposons des solutions personnalisées qui s’adaptent parfaitement à vos besoins spécifiques.
Contactez-nous dès aujourd’hui pour une analyse gratuite de vos besoins et commencez votre parcours vers l’excellence opérationnelle.



