Temps de lecture estimé : 12 minute
Table of Contents
In today’s professional world, the efficiency and clarity of internal processes are essential for maintaining high competitiveness and performance. A proven method for visualizing and optimizing these processes is the use of workflow diagrams. But what exactly is a workflow diagram and why is it so important?
Chez SMC Consulting, nous sommes spécialisés dans l’optimisation des flux de travail, l’automatisation, et l’engagement client. Dans cet article, nous allons explorer en détail ce qu’est un workflow diagramme, ses avantages, et comment vous pouvez le créer et l’utiliser pour améliorer vos processus d’entreprise.

Definition of a workflow diagram
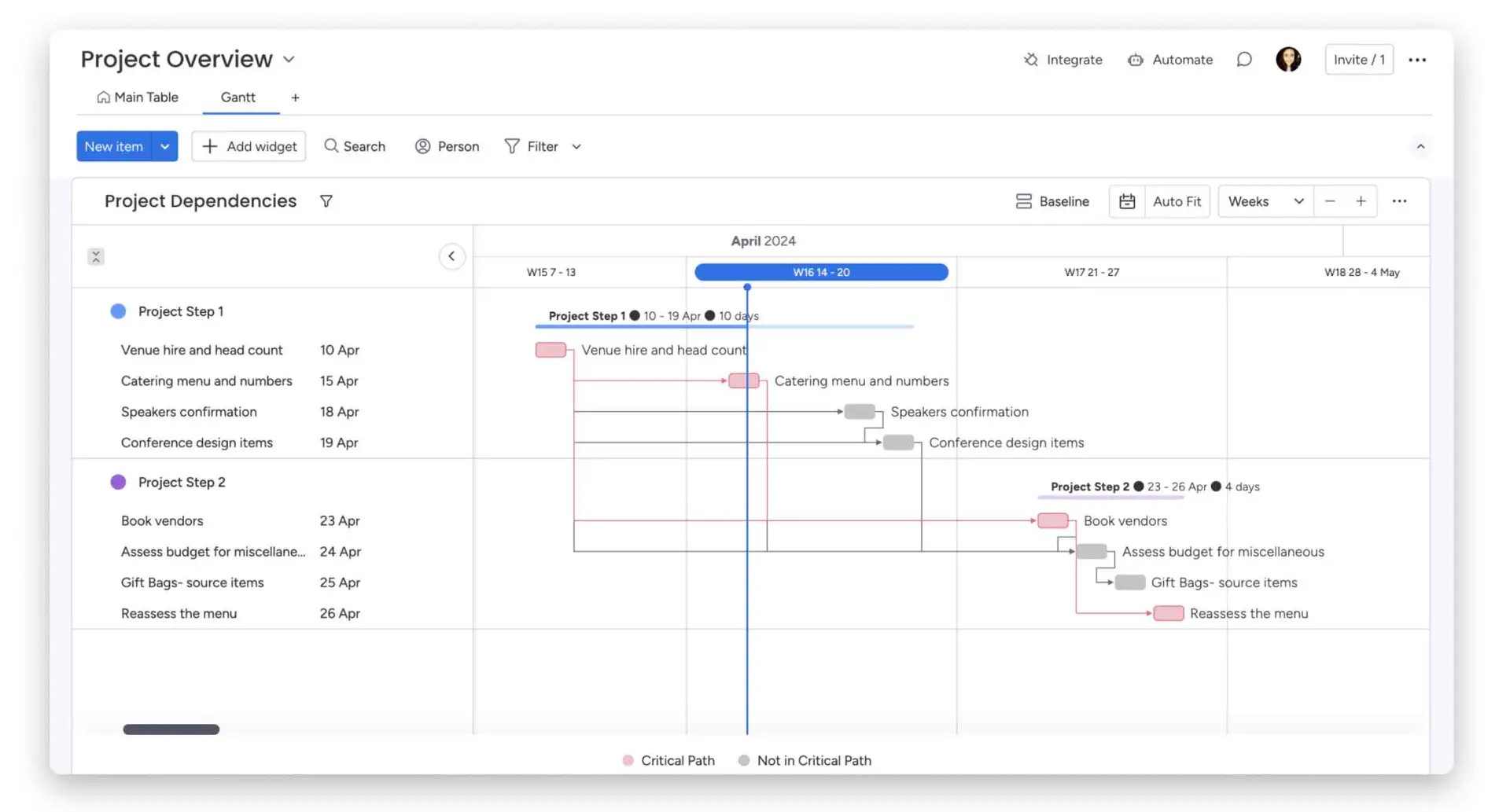
A workflow diagram is a visual representation of the steps needed to accomplish a specific task or process. It uses standardized symbols to illustrate actions, decisions, and sequences of events in a process. By visualizing workflows, businesses can identify inefficiencies, optimize procedures, and ensure smoother task execution.
Different types of workflows
There are several types of workflows, each adapted to specific needs:
- Sequential workflow: In this type of workflow, tasks are performed in a predetermined order, where each step must be completed before the next one begins. This is the simplest and most linear type of workflow.
- Parallel workflow: Here, multiple tasks can be executed simultaneously, then converge at a later stage. This allows for accelerating the overall process by performing multiple actions in parallel.
- Conditional workflow: This type of workflow incorporates decision points where the flow path can diverge based on specific conditions. It is often used to manage complex processes with multiple possible actions.
Basic terminology
To properly understand and create workflow diagrams, it’s important to familiarize yourself with some key terms:
- Steps or Activities: Represent individual actions or tasks that need to be performed in the process. They are often represented by rectangles or ovals.
- Transitions or Arrows: Indicate the direction of flow between steps, showing the order in which tasks must be accomplished. Arrows connect steps and define the workflow sequence.
- Start and End: Symbolize the starting and completion points of the workflow. The start is typically represented by a circle or oval with the word « Start », while the end is marked by a circle or oval with the word « End ».
- Decisions and Conditions: Represented by diamonds, these elements indicate points where a decision must be made, leading to alternative paths in the workflow based on specified conditions.
- Loops and Parallelisms: Illustrate repetitive tasks (loops) and tasks that can be executed simultaneously (parallelisms), often used to represent more complex processes.

Importance of workflow diagrams
Process visualization
One of the main advantages of workflow diagrams is their ability to visualize processes clearly and comprehensibly. By graphically representing each step and transition, these diagrams allow teams to see the complete work flow. This helps to better understand how tasks are interconnected, identify key steps, and easily spot potential inefficiencies or bottlenecks.
Efficiency improvement
Workflow diagrams play a crucial role in improving process efficiency. By visualizing the entire workflow, it becomes easier to identify where delays or inefficiencies occur. This allows teams to take corrective measures to optimize workflows, eliminate redundant steps, and automate repetitive tasks. Ultimately, this leads to reduced delays and better resource utilization.
Communication and collaboration
Workflow diagrams also facilitate communication and collaboration between team members. By having a visual representation of the process, all team members can clearly understand their roles and responsibilities. This reduces misunderstandings and ensures everyone is aligned on objectives and steps to follow. Additionally, these diagrams can serve as a basis for discussion during meetings to evaluate progress and plan next steps.
Documentation and standardization
Finally, workflow diagrams are essential for process documentation and standardization. They serve as an official reference for internal procedures, ensuring that all team members follow the same steps and use the same methods. This is particularly important for companies seeking to obtain or maintain quality certifications. By standardizing processes, companies can ensure increased quality and consistency in their operations.
Elements of a workflow diagram
Steps or activities
Steps or activities are the fundamental components of a workflow diagram. They represent specific actions that must be performed as part of the process. For example, in a recruitment process, steps might include « Receipt of applications », « CV selection », « Interviews », and « Job offer ». Each step must be clearly defined to ensure all stakeholders understand what needs to be done at each phase of the process.
Transitions or arrows
Transitions, often represented by arrows, connect the different steps of the workflow. They indicate the order in which tasks must be performed and show how information or tasks move from one step to another. For example, an arrow might indicate that once CVs are selected, shortlisted candidates move on to the interview stage.
Start and end
Every workflow has a starting point and an endpoint. The start, often represented by a circle or oval with the word « Start », indicates the origin of the process. The end, marked by a circle or oval with the word « End », indicates the conclusion of the process. These points clearly delineate the workflow’s scope and indicate when the process begins and ends.
Decisions and conditions
Decision points, represented by diamonds, are crucial elements in conditional workflows. They allow the workflow path to branch based on certain conditions or choices. For example, after an interview, a decision point might direct the candidate to « Job offer » if they pass the interview, or to « Application rejection » if they don’t.
Loops and parallelisms
Loops and parallelisms allow for managing repetitive tasks and simultaneous activities. A loop, indicated by an arrow returning to a previous step, represents actions repeated until a certain condition is met. Parallelisms, often represented by parallel paths, show activities that can be executed simultaneously, which is useful for accelerating the process by leveraging independent activities in parallel.
How to create a workflow diagram
Preliminary steps
Before starting to create a workflow diagram, it’s crucial to thoroughly understand the process you want to represent. This involves:
- Identify the process: Determine which process you want to model. This could be a recruitment process, project management, or customer service.
- Collect information: Gather all necessary information about process steps, involved actors, decisions to be made, and documents or tools used.
- Define objectives: Clarify the workflow’s objectives. Do you want to improve efficiency, reduce errors, or standardize procedures? These objectives will guide your diagram creation.
Choice of tools
Several tools can help you create workflow diagrams effectively:
- monday.com : Cet outil de gestion de projets offre des fonctionnalités robustes pour créer et gérer des flux de travail visuels. Il permet une collaboration en temps réel et s’intègre à de nombreux autres outils.
- Lucidchart : Un outil en ligne de création de diagrammes très intuitif, idéal pour dessiner des flux de travail détaillés. Il propose des modèles et des symboles standardisés pour faciliter le processus.
- Microsoft Visio : Un logiciel de création de diagrammes puissant, largement utilisé dans les entreprises. Il offre une grande variété de formes et de modèles pour créer des flux de travail complexes.
Diagram construction
Here are the steps to build an effective workflow diagram:
- Define key steps: List all process steps in chronological order.
- Add transitions: Use arrows to connect steps and define the process flow.
- Incorporate decision points: Add diamonds to represent points where decisions must be made, with arrows indicating different possible paths.
- Include starts and ends: Make sure to clearly mark the workflow’s beginning and end.
- Add loops and parallelisms: Represent repetitive tasks and parallel activities for a complete diagram.
Verification and validation
Once the diagram is created, it’s important to verify and validate it:
- Stakeholder review: Have team members and stakeholders review the diagram to ensure it’s complete and accurate.
- Workflow simulation: Simulate the process using the diagram to identify inefficiency points or errors.
- Adjustments: Make necessary adjustments to correct errors and optimize flow.
- Final documentation: Finalize the diagram and document it to serve as an official reference.
Use case examples
Project Management
In project management, a workflow diagram can be used to plan and track different project stages. For example, a diagram can show the steps of initial planning, task execution, progress monitoring, and project closure. This allows all team members to clearly visualize tasks to be completed and associated deadlines.
Customer service
A workflow diagram for customer service can represent the ticket management process. For example, when a customer request is received, it’s recorded as a ticket, then assigned to an agent. The agent processes the ticket, potentially requests additional information from the customer, and resolves the issue. Finally, the ticket is closed and a satisfaction survey may be sent to the customer.
HR processes
In human resources, a workflow diagram can be used to manage recruitment and onboarding processes. For example, the diagram can start with receiving applications, go through selection and interview stages, and end with new employee integration. This helps ensure each step is followed consistently and effectively.
Marketing
For a marketing campaign, a workflow diagram can help plan and execute different campaign stages. For example, the diagram might include market research, content creation, marketing material approval, campaign launch, and performance monitoring. This allows the marketing team to stay organized and ensure all campaign steps are executed in a timely manner.
Benefits of using workflow diagrams
Time savings
Workflow diagrams allow clear visualization of all process steps, which helps organize tasks more efficiently. By identifying and eliminating redundant tasks and optimizing activity sequences, businesses can significantly reduce delays. This leads to faster project and process execution, thus increasing overall productivity.
Error reduction
Workflow diagrams help identify bottlenecks and potential failure points in a process. By visualizing each step, teams can identify where errors might occur and implement controls to prevent them. This helps reduce human errors and ensure greater accuracy in task execution.
Transparency and accountability
A workflow diagram provides a clear overview of roles and responsibilities for each team member. By explicitly defining who is responsible for each step, diagrams enhance transparency and accountability. This allows each team member to know exactly what is expected of them and to whom they are accountable, thus improving coordination and collaboration.
Continuous improvement
Workflow diagrams are not static; they can be continuously reviewed and improved. By using diagrams as a basis for process evaluation, businesses can identify inefficiencies and areas needing improvement. This enables continuous improvement, adapting and optimizing workflows to meet changing needs and new challenges.
Integration with monday.com
monday.com est une plateforme de gestion de projets et de workflows largement utilisée par les entreprises pour améliorer leur efficacité opérationnelle. Avec une interface utilisateur intuitive et des fonctionnalités puissantes, monday.com permet de centraliser et de visualiser tous les aspects des projets et des processus en un seul endroit. Sa flexibilité et ses capacités de personnalisation en font un outil idéal pour la création et la gestion de workflows diagrammes.
Highlighting monday.com’s features for creating and managing workflow diagrams:
- Visual Dashboards: monday.com offers customizable dashboards that make it easy to visualize workflows and track progress in real-time.
- Task Automation: With monday.com’s automations, businesses can automate repetitive tasks, reducing errors and freeing up time for higher-value activities.
- Multiple Integrations: monday.com integrates with many other tools and systems, such as Slack, Google Drive, and Microsoft Teams, enabling seamless workflow management.
- Real-time Collaboration: The platform enables smooth team collaboration with integrated communication features like comments and notifications.
- Performance Tracking: With built-in analytics and reporting tools, monday.com allows you to track workflow performance and identify areas needing improvement.
Optimize your processes with SMC Consulting and monday.com
In today’s professional world, efficiency and clarity in internal processes are essential. Workflow diagrams prove to be powerful tools for visualizing, optimizing, and standardizing these processes. They help improve efficiency, reduce errors, and clarify roles and responsibilities.
A workflow diagram is a visual representation of the steps needed to complete a specific task or process. There are different types of workflows adapted to various needs, and their creation involves precise steps, from choosing tools to validating the diagram.
The benefits of these diagrams include time savings, error reduction, increased transparency, and continuous improvement. Tools like monday.com facilitate workflow creation and management, offering advanced features for automation and performance tracking.
At SMC Consulting, a certified monday.com partner, we support you in optimizing your workflows. We provide personalized advice and tailored solutions to improve your internal processes and ensure your success.